The Mysteries of the Heart Infographic
An infographic depicting the fascinating understandings of the human heart, as explored in HeartMath Institute’s nearly three decades of research. The ‘Did You Know?’ facts are lesser-known gems of information to enlighten curiosity on how your own thoughts and emotions are affecting yourself and others.
Download a Printable Version:
- The Mysteries of the Heart InfographicDownload (dark theme)
- The Mysteries of the Heart InfographicDownload (light theme)
The Mysteries of the Heart
A Tidbit
Research explains how the physical and energetic heart plays an extraordinary role in our lives!
Another
Tidbit
Our heart rhythms affect the brain’s ability to process information. The heart has 40,000 sensory neurons involved in relaying ascending information to the brain.
- Research explains how the physical and energetic heart plays an extraordinary role in our lives!
- Our heart rhythms affect the brain’s ability to process information. The heart has 40,000 sensory neurons involved in relaying ascending information to the brain.
Did you know?
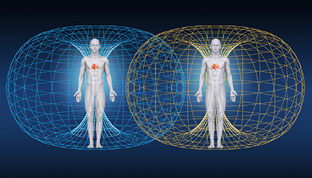
The human heart’s magnetic field can be measured several feet away from the body.
Negative emotions can create nervous system chaos, but positive emotions do the opposite.
Positive emotions can increase the brain’s ability to make good decisions.
You can boost your immune system by focusing on positive emotions.
A mother’s brainwaves can synchronize to her baby’s heartbeats even when they are a few feet apart.
Positive emotions create physiological benefits in your body.
In fetal development, the heart forms and starts beating before the brain begins to develop.
Did you know the heart has a brain of its own?
Dr. J. Andrew Armour introduced the term, "heart brain," in 1991. Armour showed that the heart’s complex nervous system qualified it as a "little brain."
The heart brain, like the brain proper, has an intricate network of neurons, neurotransmitters, proteins and support cells. It can act independently of the cranial brain and has extensive sensory capacities.
Scientists at the HeartMath Institute have conducted research on emotional energetics, coherence, heart-brain connection, heart intelligence and practical intuition.
The heart sends signals to the brain that can influence:
- perception
- emotional experience
- higher mental processes
Did you know?
Your heart emits an electromagnetic field that changes according to your emotions.
Others can pick up the quality of your emotions through the electromagnetic energy radiating from your heart.
Heart-Brain Factoids
- The heart has a system of neurons that have both short- and long-term memory, and the signals they send to the brain can affect our emotional experiences.
- The heart sends more information to the brain than the brain sends to the heart.
- Coherent heart rhythms help the brain in creativity and innovative problem-solving.

HeartMath Institute applied research is solution-oriented.
83%said they felt healthier†
69%said they have more energy and vitality†
33%reported sleeping better†
† These percentages are based on 5,000 assessments of individuals who used HeartMath techniques and the emWave® technology.
These facts are brought to you by the HeartMath Institute Research Center, where ongoing research is being conducted to help explain the connection and role of the heart in our emotion-based experiences.

Sources
-
Science of the Heart: Exploring the Role of the Human Heart in Human Performance
https://heartmath.org./
resources/downloads/ science-of-the-heart/ -
Neurocardiology: Anatomical and Functional Principles by J. Andrew Armour, M.D., Ph.D.
-
The Electricity of Touch: Detection and Measurement of Cardiac Energy Exchange Between People by Rollin McCraty, Ph.D., Mike Atkinson, Dana Tomasino, B.A., and William A. Tiller, Ph.D.
https://heartmath.org./research/
research-library/energetics/ electricity-of-touch/ -
HeartMath Institute’s free resources, tools and techniques for well-being, assessments tools, Articles of the Heart Library and Solutions For Stress Index, go to:
-
Stress Fact, Global Organization for Stress